Services
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy
- Endoscopic Procedures (Keyhole Surgery)
- Fastest Laparoscopic Procedures
- Hysteroscopic Surgeries
- Laparoscopic Fertility Promoting Surgery
- Laparoscopic Gynaecological Surgery
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
- Laparoscopic Operative Procedures
- Laparoscopic Reproductive Surgery
Laparoscopic Operative Procedures:
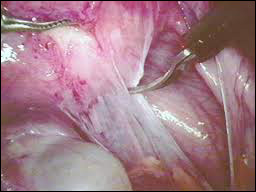 Laparoscopic Adhesiolysis
Laparoscopic Adhesiolysis
Adhesions are strands of tissue that form in the body in response to injury. Abdominal cavity is one of the commonest sites where adhesions tend to form. Looking for them through a laparoscope is the only way confirming their presence. In fact, no other test or investigation can diagnose adhesions with certainty. If the surgeon encounters adhesions, they can be easily divided using long laparoscopic instruments. The procedure is called adhesiolysis. A patient recovers quickly after laparoscopic surgery for adhesions as she has very little pain.
What are the advantages of laparoscopic adhesiolysis?
- Less pain from the incisions after surgery
- Less postoperative medication used
- Almost no chance of having hernia
- Shorter hospital stay
- Shorter recovery time
- Faster return to normal diet
- Faster return to work or normal activity
- Better cosmetic healing
- Lower chance of re-formation of the adhesions
Laparoscopic Endometriotic Intervention
Laparoscopy is the most common procedure used to diagnose and remove mild to moderate endometriosis. If your doctor recommends a laparoscopy, it will be to:
 View the internal organs to look for signs of endometriosis and other possible problems. This is the only way that endometriosis can be diagnosed with certainty. But a “no endometriosis” diagnosis is never certain. Growths (implants) can be tiny or hidden from the surgeon’s view.
View the internal organs to look for signs of endometriosis and other possible problems. This is the only way that endometriosis can be diagnosed with certainty. But a “no endometriosis” diagnosis is never certain. Growths (implants) can be tiny or hidden from the surgeon’s view.
- Remove any visible endometriosis implants and scar tissue that may be causing pain or infertility. If an endometriosis cyst is found growing on an ovary (endometrioma), it is likely to be removed.
Laparoscopic Ovarian Cyst Operation
 Laparoscopic cystectomy is the preferred approach to managing benign ovarian cysts in adolescents and adults. A retrospective study of 282 females aged 25 years or younger who underwent laparoscopic surgery concluded that the procedure is a safe first-line strategy for cysts in this age group.
Laparoscopic cystectomy is the preferred approach to managing benign ovarian cysts in adolescents and adults. A retrospective study of 282 females aged 25 years or younger who underwent laparoscopic surgery concluded that the procedure is a safe first-line strategy for cysts in this age group.
The advantages of laparoscopy over traditional abdominal ovarian cystectomy surgery include a shorter post-operative hospital stay, a shorter recovery interval and less pain. Also since smaller instruments are used, more ovarian tissue can be spared and scarring can be minimized.
Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling is a surgical treatment that can trigger ovulation in women who have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Electrocautery or a laser is used to destroy parts of the ovaries.
This surgery is not commonly used. But it can be an option for women who are still not ovulating after losing weight and trying fertility medicines. Destroying part of the ovaries may restore regular ovulation cycles.
Laparoscopic Tubal Recanalization
Laparoscopic tubal ligation is the most common form of female birth control. Although it is a permanent form of sterilization, some women ask for reversal of the process. Laparoscopy is the most widely used procedure for Tubal Recanalization. The major advantage is speedy recovery with minimal tissue handling. The process is performed under a general anesthesia.
After successful recanalization the patients are advised to try for conception from the next menstrual cycle. The fertility outcomes are favorable and it is a preferred method in many fertility centers.
Laparoscopic Myomectomy
 The advantage of a laparoscopic myomectomy over an abdominal myomectomy is that several small incisions are used rather than one larger incision. Laparoscopic surgery is usually performed as out-patient surgery under general anesthesia. The procedure can take one to three hours, depending on the number, size, and depth of the fibroids within the muscle wall. Because the incisions are small, recuperation is usually associated with minimal discomfort.
The advantage of a laparoscopic myomectomy over an abdominal myomectomy is that several small incisions are used rather than one larger incision. Laparoscopic surgery is usually performed as out-patient surgery under general anesthesia. The procedure can take one to three hours, depending on the number, size, and depth of the fibroids within the muscle wall. Because the incisions are small, recuperation is usually associated with minimal discomfort.
Fibroids that are attached to the outside of the uterus by a stalk (pedunculated fibroids) are the easiest to remove laparoscopically. Many subserous fibroids (close to the outer surface) can also be removed through the laparoscope.
Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation
 Laparoscopic tubal ligation is a surgical sterilization procedure in which a woman’s fallopian tubes are either clamped and blocked or severed and sealed. Both methods prevent eggs from being fertilized. Tubal ligation is a permanent method of sterilization.
Laparoscopic tubal ligation is a surgical sterilization procedure in which a woman’s fallopian tubes are either clamped and blocked or severed and sealed. Both methods prevent eggs from being fertilized. Tubal ligation is a permanent method of sterilization.
Tubal ligation can be performed in the peripartum period or at any time remote from pregnancy (referred to as interval sterilization). Approximately half of female sterilizations are interval sterilizations, and the other half are performed at the time of cesarean delivery or immediately postpartum. Most interval sterilizations are performed laparoscopically.
Laparoscopic tubal ligation has many advantages that explain its use as the interval procedure of choice. It offers the opportunity to explore pelvic and abdominal anatomy, especially if the patient has complaints such as pelvic pain. The procedure is an outpatient surgery with a rapid recovery, allowing patients to return quickly to work or home.
Laparoscopic Ectopic Pregnancy Operation
At any stage of development, surgical removal of an ectopic growth and/or the fallopian tube section where it has implantedis the fastest treatment for ectopic pregnancy. Surgery may be your only treatment option if you have internal bleeding. When possible, surgery is done through a small incision using laparoscopy. This type of surgery usually has a short recovery period.
An ectopic pregnancy can be removed from a fallopian tube by using salpingostomy or salpingectomy.
- Salpingostomy. The ectopic growth is removed through a small, lengthwise cut in the fallopian tube (linear salpingostomy). The cut is left to close by itself or is stitched closed.
- Salpingectomy. A fallopian tube segment is removed. The remaining healthy fallopian tube may be reconnected. Salpingectomy is needed when the fallopian tube is being stretched by the pregnancy and may rupture or when it has already ruptured or is very damaged.
When an ectopic pregnancy is located in an unruptured fallopian tube, every attempt is made to remove the pregnancy without removing or damaging the tube.
Emergency surgery is needed for a ruptured ectopic pregnancy.
Laparoscopic Chromopertubation
 Chromopertubation is a procedure usually done during a laparoscopy to visualize the fallopian tubes in order to see if they are patent or open. It’s done during an infertility work-up. It is a procedure where a colored dye is passed through the fallopian tubes to confirm that they are patent. The procedure is done under anesthesia and during laparoscopy.
Chromopertubation is a procedure usually done during a laparoscopy to visualize the fallopian tubes in order to see if they are patent or open. It’s done during an infertility work-up. It is a procedure where a colored dye is passed through the fallopian tubes to confirm that they are patent. The procedure is done under anesthesia and during laparoscopy.
A chromopertubation may be called for if a patient is undergoing a surgical procedure where the fallopian tubes are visible. A dye can be introduced into the uterine cavity being injected through the cervical canal during the procedure and then observed as it comes out of the ends of the tubes into the peritoneal (abdominal) cavity.
Sometimes tubal occlusion as well as adhesions cannot be detected completely by looking at the fallopian tubes, so additional tests may be necessary to provide a full evaluation.



