Services
- Diagnostic Laparoscopy
- Endoscopic Procedures (Keyhole Surgery)
- Fastest Laparoscopic Procedures
- Hysteroscopic Surgeries
- Laparoscopic Fertility Promoting Surgery
- Laparoscopic Gynaecological Surgery
- Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
- Laparoscopic Operative Procedures
- Laparoscopic Reproductive Surgery
Hysteroscopic Surgeries:
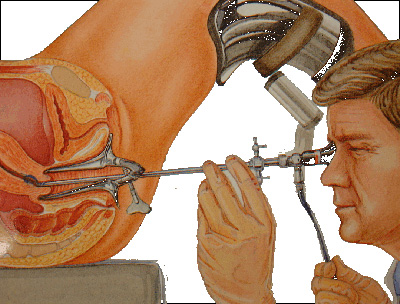 Hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows your doctor to look inside your uterus in order to diagnose and treat causes of abnormal bleeding. Hysteroscopy is done using a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube that is inserted into the vagina to examine the cervix and inside of the uterus. Hysteroscopy can be either diagnostic or operative.
Hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows your doctor to look inside your uterus in order to diagnose and treat causes of abnormal bleeding. Hysteroscopy is done using a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube that is inserted into the vagina to examine the cervix and inside of the uterus. Hysteroscopy can be either diagnostic or operative.
What is diagnostic hysteroscopy?
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is used to diagnose problems of the uterus. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is also used to confirm results of other tests, such as hysterosalpingography (HSG). HSG is an X-ray dye test used to check the uterus and fallopian tubes. Diagnostic hysteroscopy can many times be done in an office setting.
Additionally, hysteroscopy can be used with other procedures, such as laparoscopy, or before procedures such as dilation and curettage (D&C). In laparoscopy, your doctor will insert an endoscope (a slender tube fitted with a fiber optic camera) into your abdomen to view the outside of your uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes. The endoscope is inserted through an incision made through or below your navel.
What is operative hysteroscopy?
Operative hysteroscopy is used to correct an abnormal condition that has been detected during a diagnostic hysteroscopy. If an abnormal condition was detected during the diagnostic hysteroscopy, an operative hysteroscopy can often be performed at the same time, avoiding the need for a second surgery. During operative hysteroscopy, small instruments used to correct the condition are inserted through the hysteroscope.
When is operative hysteroscopy used?
Your doctor may perform hysteroscopy to correct the following uterine conditions:
- Polyps and fibroids —Hysteroscopy is used to remove these non-cancerous growths found in the uterus.
- Adhesions —Also known as Asherman’s Syndrome, uterine adhesions are bands of scar tissue that can form in the uterus and may lead to changes in menstrual flow as well as infertility. Hysteroscopy can help your doctor locate and remove the adhesions.
- Septums— Hysteroscopy can help determine whether you have a uterine septum, a malformation of the uterus that is present from birth.
- Abnormal bleeding— Hysteroscopy can help identify the cause of heavy or lengthy menstrual flow, as well as bleeding between periods or after menopause. Endometrial ablation is one procedure in which the hysteroscope, along with other instruments, is used to destroy the uterine lining in order to treat some causes of heavy bleeding.
- Insertion of hormone containing IUCD – In conditions like abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) if hysteroscopy no definite uterine pathology is seen nowadays a hormone containing IUCD is inserted with hysteroscope inside the uterine cavity. This IUCD has got a life of 5 years, during which it releases continuous low but measured dose of hormone acting inside the uterine cavity controlling the abnormal bleeding. It is also the internationally accepted mode of treatment for adenomyosis (where uterus is enlarged, giving rise to a painful menstrual period). Most importantly, these IUCDs do not have any systemic side effect on any part of the body.
What are the benefits of hysteroscopy?
Compared with other, more invasive procedures, hysteroscopy may provide the following advantages:
- Shorter hospital stay
- Shorter recovery time
- Less pain medication needed after surgery
- Avoidance of hysterectomy
- Possible avoidance of “open” abdominal surgery
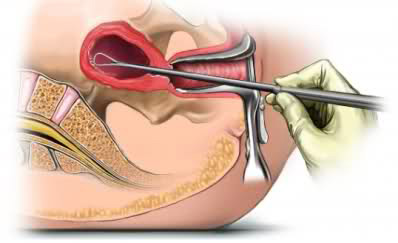 When should the procedure be performed?
When should the procedure be performed?
Your doctor may recommend scheduling the hysteroscopy for the first week after your menstrual period. This timing will provide the doctor with the best view of the inside of your uterus. Hysteroscopy is also performed to determine the cause of unexplained bleeding or spotting in postmenopausal women.
What type of anesthesia is used for hysteroscopy?
Anesthesia for hysteroscopy may be local, regional, or general:
- Local anesthesia –the numbing of only a part of the body for a short time
- Regional anesthesia –the numbing of a larger portion of the body for a few hours
- General anesthesia –the numbing of the entire body for the entire time of the surgery
How is hysteroscopy performed?
Prior to the procedure, your doctor may prescribe a sedative to help you relax. You will then be prepared for anesthesia. The procedure itself takes place in the following order:
- The doctor will dilate (widen) your cervix to allow the hysteroscope to be inserted.
- The hysteroscope is inserted through your vagina and cervix into the uterus.
- Carbon dioxide gas or a liquid solution is then inserted into the uterus, through the hysteroscope, to expand it and to clear away any blood or mucus.
- Next, a light shone through the hysteroscope allows your doctor to see your uterus and the openings of the fallopian tubes into the uterine cavity.
- Finally, if surgery needs to be performed, small instruments are inserted into the uterus through the hysteroscope.
The time it takes to perform hysteroscopy can range from less than 5 minutes to more than an hour. The length of the procedure depends on whether it is diagnostic or operative and whether an additional procedure, such as laparoscopy, is done at the same time. In general, however, diagnostic hysteroscopy takes less time than operative.
What can I expect after the procedure?
If regional or general anesthesia is used during your procedure, you may have to be observed for several hours before going home. After the procedure, you may have some cramping or slight vaginal bleeding for one to two days. In addition, you may feel shoulder pain if gas was used during your hysteroscopy. It is also not unusual to feel somewhat faint or sick. However, if you experience any of the following symptoms, be sure to contact your doctor:
- Fever
- Severe abdominal pain
- Heavy vaginal bleeding or discharge
Will I have to stay in the hospital overnight?
Hysteroscopy is considered minor surgery and usually does not require an overnight stay in the hospital. However, in certain circumstances, such as if your doctor is concerned about your reaction to anesthesia, an overnight stay may be required.



